What is a rare disease?
A rare disease, also known as an orphan disease, is a medical condition that affects a small number of people. In most countries, a disease is considered rare when it affects fewer than 1 in 2,000 individuals. However, this definition may vary from country to country.
Rare diseases can be genetic, meaning they are caused by an alteration or mutation in a person’s genes, or they can be acquired later in life due to infections, environmental factors, or other causes. These conditions are often chronic, progressive, and potentially life-threatening. They can have a wide range of symptoms and affect various organs and systems in the body.
Examples of rare diseases
1. Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. This rare genetic disorder causes rapid aging in children, resulting in a variety of health issues.
2. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. A condition in which soft tissues progressively turn into bone, resulting in loss of mobility and a second skeleton.
3. Stiff person syndrome. A neurological disorder characterized by muscle stiffness and spasms that can lead to difficulty moving or walking.
4. Prader-Willi syndrome. A complex genetic disorder that affects various aspects of physical and mental development, including compulsive overeating and obesity.
5. Harlequin ichthyosis. A severe genetic skin disorder that causes the skin to become thick, dry, and scaly, resulting in deep cracks and deformities.
6. Alice in Wonderland syndrome. A neurological condition characterized by a distorted perception of the body or surrounding objects, often leading to a sense of size distortion and hallucinations.
7. Auto-brewery syndrome. A rare condition in which the body ferments carbohydrates into alcohol, leading to symptoms similar to being intoxicated even without consuming alcoholic beverages.
8. Alien hand syndrome. A neurological disorder in which a person’s hand shows autonomous, involuntary movements that are sometimes contradictory to their intentions.
9. Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome: A group of rare autoimmune disorders that affect multiple endocrine glands and lead to hormonal imbalances.
10. Cotard’s syndrome. Also known as “walking corpse syndrome,” this rare psychological disorder causes sufferers to believe that they are dead or do not exist.
Challenges of rare disease research
According to the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, rare diseases are estimated to affect over 30 million people in the United States. Since individual rare diseases affect a small number of people, there is limited knowledge about their causes, diagnosis, treatment, and potential cure. This can lead to delayed or incorrect diagnosis, lack of effective treatments, and limited support or resources for patients and their families.
In 2019, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first gene therapy, Zolgensma, for the treatment of SMA. This breakthrough has shown promising results in improving the health and prolonging the lives of infants with this rare genetic disorder. So far, some promising areas of research and technological advancements could further lead to significant progress in rare disease research in the coming years.
Due to their rarity, rare diseases often face challenges in research funding, clinical trials, and access to specialized healthcare services. Efforts are being made globally to raise awareness about rare diseases, improve diagnostics and therapies, and provide support to patients and families affected by these conditions.
Rare disease diagnosis technologies
Rare disease diagnosis can often be a complex and time-consuming process. Many rare diseases have symptoms that overlap with more common conditions, causing misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. Additionally, traditional diagnostics methods may not be suitable for these diseases, as they often require specialized tests that are not widely available.
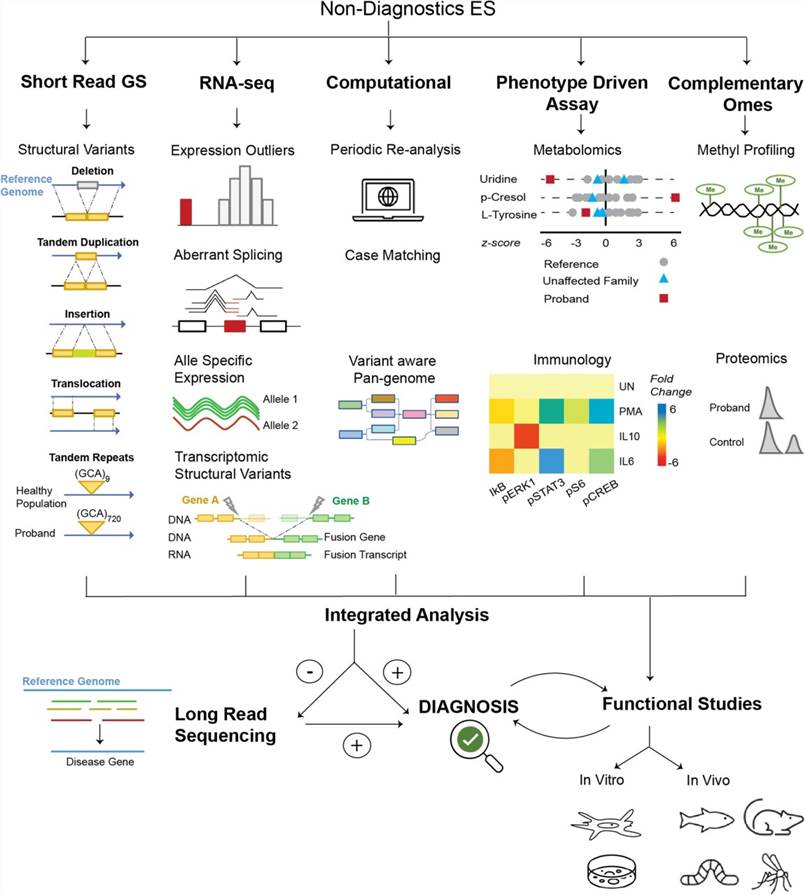
In recent years, however, there has been a surge in the development of new diagnostic tools and technologies aimed specifically at rare diseases. These innovative approaches include genetic testing, next-generation sequencing, and biomarker analysis. These technologies allow for more accurate and early detection of rare diseases by analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup or identifying specific biomarkers in their blood or tissues.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is one such breakthrough in diagnostics that has revolutionized the field of rare diseases. By analyzing an individual’s DNA, scientists can identify variations or mutations that are associated with certain rare disorders. This technology has enabled healthcare professionals to pinpoint the cause of rare diseases more accurately and tailor treatments specific to each patient’s genetic makeup.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has further enhanced the diagnostic process. This technique allows for rapid and cost-effective sequencing of multiple genes simultaneously. With NGS, scientists can examine a large number of genes associated with various rare diseases. Providing a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s genetic profile, further boosting the chances of identifying a genetic abnormality that answers the diagnostic puzzle.
In addition to gene technology, biomarker analysis has also become a valuable tool in the fight against rare diseases. Biomarkers are measurable substances present in the body that can indicate the presence or progression of a particular disease. By analyzing these biomarkers in a patient’s blood or tissue samples. Researchers can gain valuable insights into the underlying pathology or detect the disease at an early stage.
The significant advantage of these innovative diagnostic approaches is their ability to detect rare diseases at an earlier stage. Increasing the chances of successful intervention. With the continuous innovation in these technologies, diagnostic development is expected to accelerate rare disease therapy development worldwide.